聴覚評価と耳鏡検査 – OSCEガイド
聴覚評価と耳鏡検査はOSCEで頻繁に登場し、あなたの臨床検査スキルで関連する兆候を特定することが要求されるでしょう。
はじめに
手を洗い、必要に応じてPPEを着用します。
名前と役割を含めて患者に自己紹介します。
患者の名前と誕生日を確認します。
患者に優しい言葉を用いて、検査内容を簡潔に説明します。 「今日はあなたの耳を診察したいと思います。耳鏡という特殊な器具を使って、あなたの耳の中を見てみたいと思います。
検査を行うことに同意してもらいます。
椅子に座るように患者にお願いします。
臨床検査を行う前に、患者に痛みがあるかどうか聞いておきます。
一般検査
物品や設備
病歴や現在の臨床状態について有益な洞察を与える可能性のある、患者上または周囲の物品や設備を探す:
- 補聴器:患者が補聴器をつけているか注意し、耳鏡検査を行う際にはこれを外すよう患者に頼む。
- 移動補助器具:車椅子や歩行器などの物品から、患者の現在の移動状態をうかがう。
聴力評価
準備
患者に、最近聴力に変化があったかを尋ねます。
これから3つの単語または3つの数字を言うので、患者にそれを繰り返してもらいたいと説明する(2音節の単語または2桁の数字を選ぶ)
評価
1.
1.患者の耳から約60cmの位置に立ち、数字や単語をささやく。
2.耳介をさすることで検査しない方の耳をふさぐ。
3.耳朶を擦るときは、腕を患者の顔に当てないようにしましょう。
3.患者に数字や単語を復唱してもらいます。 3分の2以上が正しく聞き取れれば、聴力は12db以上です。
4.反応がない場合は、15cmまで近づいてテストを繰り返すことができます。 ここでは、囁き声では34db、会話音声では56dbを閾値としています。
5. もう片方の耳も同じように評価します。
-
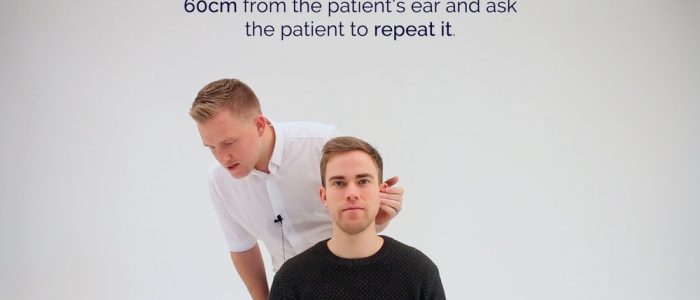 Whisper a number 60cm from the ear
Whisper a number 60cm from the ear
Weber’s test
Explain to the patient that you are going to test their hearing using a tuning fork.
1. Tap a 512Hz tuning fork and place in the midline of the forehead. The tuning fork should be set in motion by striking it on your knee (not the patient’s knee or a table).
2. Ask the patient “Where do you hear the sound?”
These results should be assessed in context with the results of Rinne’s test before any diagnostic assumptions are made:
- Normal: sound is heard equally in both ears.
- Sensorineural deafness: sound is heard louder on the side of the intact ear.
- Conductive deafness: sound is heard louder on the side of the affected ear.
A 512Hz tuning fork is used as it gives the best balance between time of decay and tactile vibration. Ideally, you want a tuning fork that has a long period of decay and cannot be detected by vibration sensation.
-
 Tap a 512Hz tuning fork and place in the midline of the forehead
Tap a 512Hz tuning fork and place in the midline of the forehead
Rinne’s test
1. Place a vibrating 512 Hz tuning fork firmly on the mastoid process (apply pressure to the opposite side of the head to make sure the contact is firm).
2.患者が音叉の音を聞くことができることを確認し、いつ聞こえなくなるかを教えてもらいます。
3.患者が音を聞くことができなくなったら、音叉を外耳道の前に移動して空気伝道をテストします。
4.今また音が聞こえるか患者に尋ねます。
4.音が聞こえるようになったかどうか、患者に尋ねる。音が聞こえるようなら、空気伝導が骨伝導より優れていることを示唆しており、これは健康な人に期待されることである(これはしばしば「リンネの陽性」結果と混同されることがある)。
リンネのテスト結果のまとめ
これらの結果は、診断上の仮定を行う前に、ウェーバー テストの結果との関連で評価されるべきです:
- 正常な結果です。 air conduction > bone conduction (Rinne’s positive)
- Sensorineural deafness: air conduction > bone conduction (Rinne’s positive) – due to both air and bone conduction being reduced equally
- Conductive deafness: bone conduction > air conduction (Rinne’s negative)
-
 Place a 512 Hz tuning fork on the mastoid process
Place a 512 Hz tuning fork on the mastoid process
伝音難聴と感音難聴
外耳、外耳道、鼓膜、中耳(小骨)の間のどの場所でも音が有効に伝わらなくなると、伝音難聴と呼ばれるようになります。
伝音難聴は、蝸牛や前庭神経の機能障害によって起こります。 感音難聴の原因としては、加齢(老眼)、過度の騒音への暴露、遺伝子変異、ウイルス感染(サイトメガロウイルスなど)、耳毒性物質(ゲンタマイシンなど)などが挙げられます。
外耳炎
検査
親骨
親骨の検査
- 非対称:親骨を比較することにより、微妙な片側の病理を特定できる場合があります。
- 耳介の変形:後天性(例:カリフラワー耳)または先天性(例:無耳症、小耳症、低位耳)
- ピアス:感染源、アレルゲン、外傷の原因となる可能性がある
- 発赤および水腫:一般的に外耳炎に関連する。
- 瘢痕:以前の手術を示す。
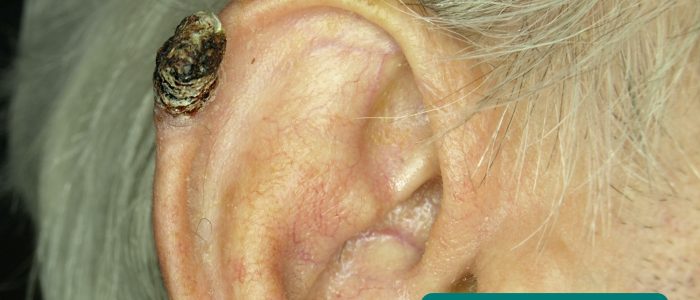
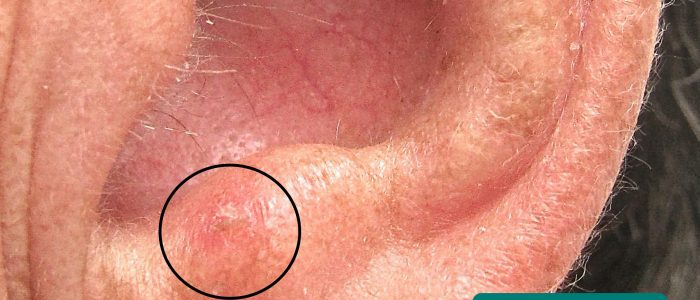
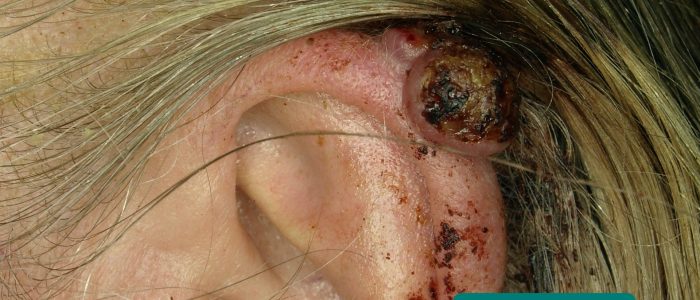
- 皮膚病変:前悪性腫瘍(光線性角化症)および悪性腫瘍(例:基底細胞癌、扁平上皮癌)の皮膚変化の証拠を探す。
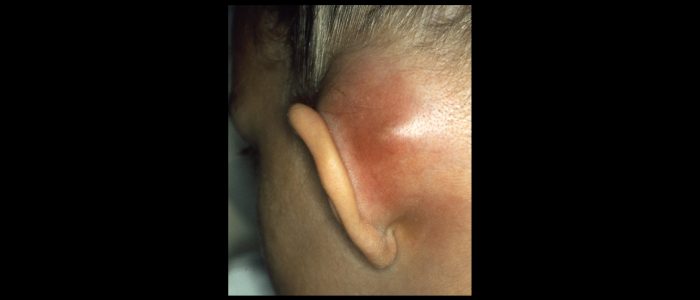
乳様体
乳様体を調べる:
- 乳房炎と関連して、典型的には紅斑および膨潤がある。
- 瘢痕:以前の手術(例:乳様突起切除術)を示す。
耳前部
耳前部(耳の前)を検査する:
- 耳前洞/孔:耳前部にくぼみとして現れる、一般的な先天性の奇形である。 These sinuses can sometimes become infected and require surgical drainage.
- Lymphadenopathy: typically associated with an ear infection (e.g. otitis media, otitis externa).
Conchal bowl
Inspect the conchal bowl for signs of active infection such as erythema and purulent discharge.
Palpation
Palpate the tragus for tenderness which is typically associated with otitis externa.
Palpate the regional lymph nodes:
- Pre-auricular lymph nodes
- Post-auricular lymph nodes
-
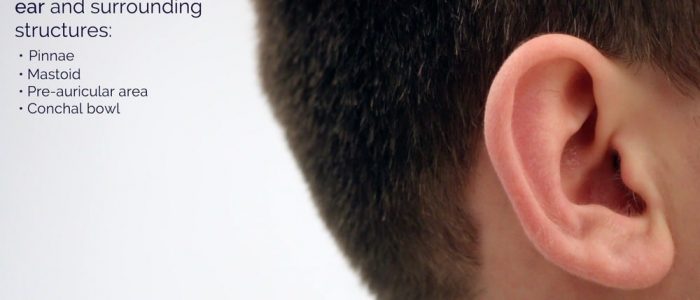
 Anatomy of the ear
Anatomy of the ear
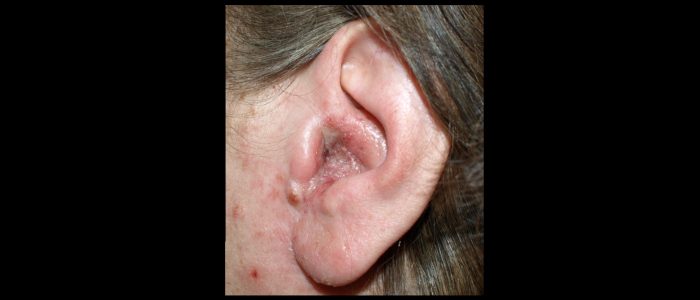
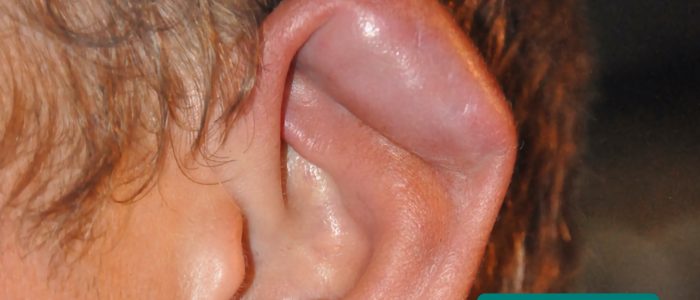
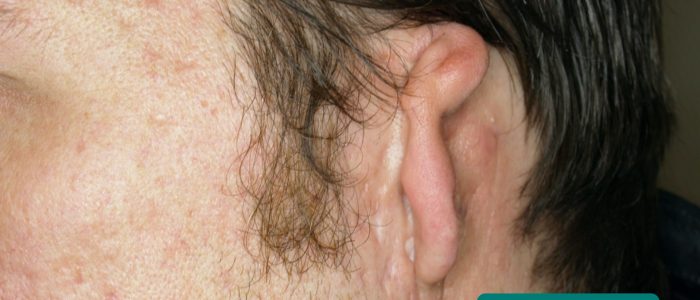
Cauliflower ear
Cauliflower ear is an irreversible condition that develops as a result of repeated blunt ear trauma. Blunt trauma causes bleeding under the perichondrium of the pinna, stripping away the ear’s cartilage. This cartilage normally relies on the perichondrium for its nutrient supply and as a result, once separated it becomes fibrotic, causing distortion of the ear’s architecture.
Congenital deformity of the ears
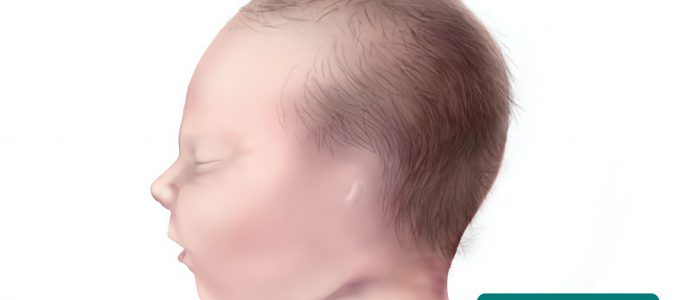
There are several types of congenital ear deformity including:
- Anotia: a complete absence of the pinna.
- Microtia: underdevelopment of the pinna.
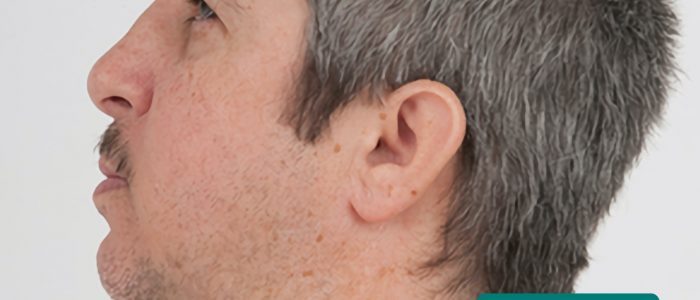
- Low-set ears: the ears are positioned lower on the head than usual. 低位耳は、ダウン症やターナー症候群を含むいくつかの遺伝的症候群の特徴です。
耳鏡検査
最初に検査する耳を決めるために:
- 患者に耳の不快感があるかどうか確認し、もしあれば痛みのない側を最初に検査します。
- 患者にどちらが「良い」耳か尋ね、まずこちらを検査します(これは比較に役立ちます)
耳鏡の挿入
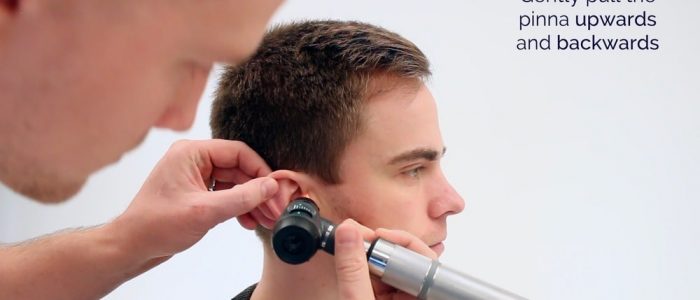
1.耳鏡の挿入。
1.耳鏡のライトが機能していることを確認し、滅菌した鏡(外耳道に楽に収まる大きさ)を当てます。
2.もう一方の手で耳介を上下に引き、外耳道をまっすぐにします。
- 耳鏡は、患者の右耳の場合は右手に、左耳の場合はその逆にしてください。
4.直視下で耳鏡の前進を行います。
外耳道の評価
5.
- 過剰な耳垢:伝音難聴の最も一般的な原因
- 紅斑と水腫:一般的に外耳炎に関連します
- 放電:外耳炎または鼓膜穿孔を伴う中耳炎の可能性が示唆されます。
- 異物:綿棒、昆虫、その他の小さなものを含むことがあります。
鼓膜の評価
6. 病気の見逃しを防ぐため、鼓膜の4象限を系統的に検査します。
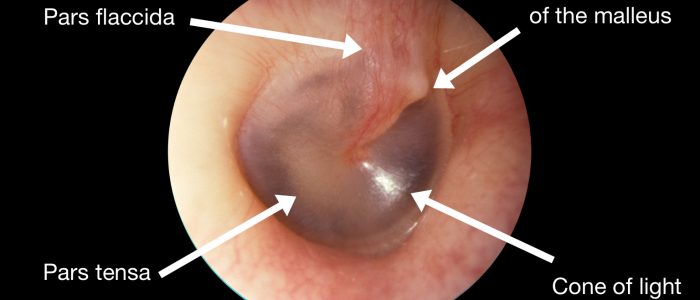
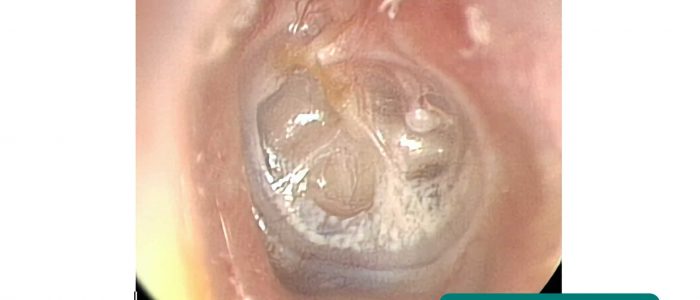
色
健康な鼓膜は、真珠色で半透明なように見えます。
紅斑は、急性中耳炎などで起こりうる鼓膜の炎症を示唆します。
形状
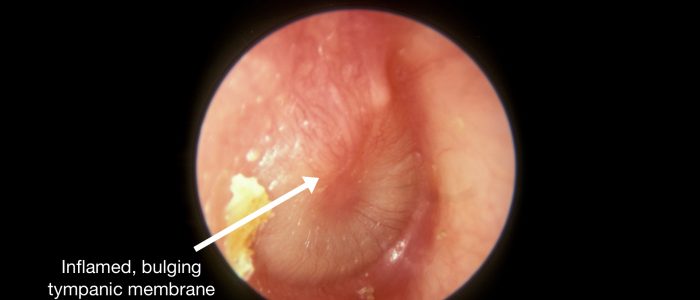
健康な鼓膜は、比較的平らに見えます。
鼓膜の膨隆は、中耳圧の上昇を示唆し、これは一般に滲出液を伴う急性中耳炎によって引き起こされます (しばしば目に見える液量が存在します)。
中耳腔の後退は、中耳圧の低下を示唆します。これは、上気道感染症やアレルギーによる咽頭鼓膜チューブ機能不全によってよく起こります。
光反射
光反射 (「光のコーン」としても知られています) は、光が中耳に照射されるときに見ることができます。
顎関節が健康であれば、円錐状の光の反射は前下方に現れるはずです。
左耳では、光の反射はおよそ7時~8時の位置にあるはずです。
右耳では、光の反射はおよそ4時~5時の位置にあるはずです。
光反射の欠如または歪みは、(顎骨の膨張による)中耳炎と関連しています。
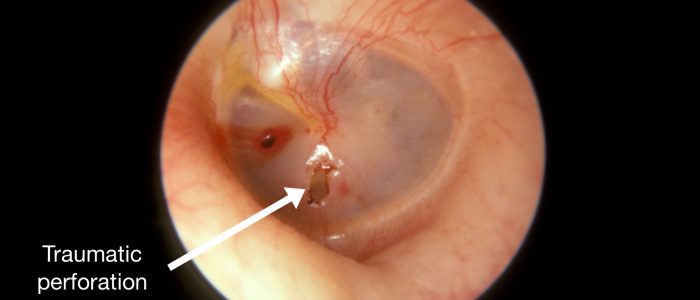
穿孔
顎骨の穿孔のサイズと位置に注意します。
顎骨穿孔の原因には、感染(例:浸出を伴う中耳炎)、外傷(例:膿胸)があります。
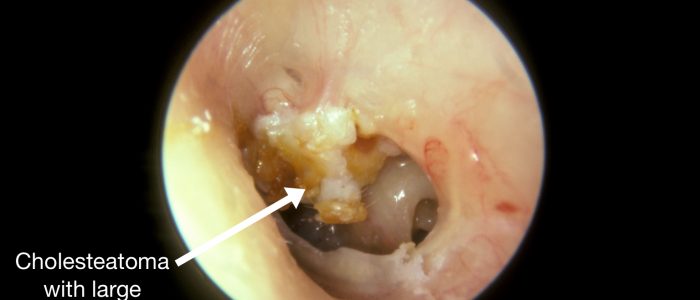
真珠腫は一般に、鼓膜の上部に穴を開け、この部分に肉芽組織や分泌物が見えることがあります。
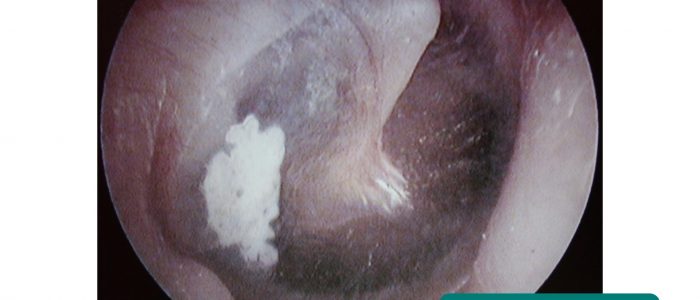
瘢痕
鼓膜の瘢痕化は鼓膜硬化として知られており、それが広範囲であれば、重大な伝導難聴になる可能性があります。
中耳炎や鼓膜切開チューブの挿入後に、鼓膜硬化症が発症することがよくあります。
最終ステップ
7、耳鏡は慎重に引き出します。
8、所見を比較しながら、もう一方の耳も評価します。
8.もう片方の耳でも評価を繰り返し、所見を比較します。片方の耳に感染がある場合は、もう片方の耳を検査する前に耳鏡の鏡体を交換します。 耳鏡の鏡は臨床廃棄物容器に捨てる。
-
 Prepare the otoscope
Prepare the otoscope
Otitis media and otitis externa
Acute otitis media is an inflammatory condition of the middle ear that can be caused by viruses and bacteria. Typical findings on otoscopy include a bulging red, yellow or cloudy tympanic membrane with an associated air-fluid level behind the membrane. There may also be discharge in the auditory canal if the tympanic membrane has perforated.
Otitis externa is an inflammatory condition of the outer ear that can affect the auricle, external auditory canal and external surface of the tympanic membrane. The condition is usually caused by a bacterial infection. 典型的な検査所見としては、耳介および外耳道の紅斑とそれに伴う疼痛が挙げられます。 その他の所見としては、狭窄を引き起こす聴管の水腫、局所リンパ節腫脹、外耳道内の分泌物などがあります。
検査を終了するには…
患者さんに、これで検査が終了したことを説明します。
患者にお礼を言う
PPEを適切に廃棄し、手を洗う
所見をまとめる
まとめ例
「今日は25歳の男性、スミスさんを診察しました。 全身検査では安静時に快適そうで、外耳の検査では異常は認められなかった」
「耳鏡検査では鼓膜と聴管が正常であった」
「耳鏡検査では鼓膜と聴管が正常であった。 There was no evidence of hearing loss on assessment.”
“In summary, these findings are consistent with a normal examination of the ears.”
“For completeness, I would like to perform the following further assessments and investigations.”
Further assessments and investigations
- Cranial nerve examination: to identify evidence of facial nerve pathology.
- Audiometry and tympanometry: to screen for hearing loss.
Reviewers
Mr Krishan Ramdoo
ENT Registrar
Mr Ben Cosway
ENT Registrar
Show references
- CNX OpenStax. Geeky Medicsによって翻案された。 Otitis externa. ライセンス .
- B. Welleschik. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 Mastoiditis. ライセンス CC BY-SA.
- Klaus D. Peter、Gummersbach、Germany. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 Basal cell carcinoma. ライセンス: CC BY 3.0 DE.
- Future FamDoc. Geeky Medicsによって翻案された。 Actinic keratosis. ライセンス CC BY-SA.
- Klaus D. Peter, Gummersbach, Germany. Geeky Medicsによって翻案された。 メラノーマ。 ライセンス。 CC BY 3.0 DE.
- MartialArtsNomad.com. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 カリフラワー・イヤー。 Licence: CC BY.
- Lisa Leathwood, Maureen Risch. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 低く設定された耳。 Licence: CC0.
- Klaus D. Peter、Gummersbach、ドイツ。 Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 小耳症。 Licence: CC BY 3.0 DE.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities(米国疾病対策予防センター、出生時障害および発達障害に関する国立センター)。 Geeky Medicsによって採用されました。 Anotia.
- By Michael Hawke MD. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 正常な鼓膜。 ライセンス:.
- By Michael Hawke MD. Geeky Medicsによって翻案されました。 鼓膜穿孔。 ライセンス: .
- By Michael Hawke MD. Adapted by Geeky Medics. 耳管腫。 ライセンス:.
- By Michael Hawke MD. Adapted by Geeky Medics. 急性中耳炎。 ライセンス:.
- Didier Descouens。 Adapted by Geeky Medics. 鼓膜硬化症。 Licence: CC BY-SA.
- Adrian L James. Adapted by Geeky Medics. Tympanic membrane retraction. Licence: CC BY-SA.